简介
官方文档:
Spring Cloud OpenFeign
OpenFeign和Feign的区别:
feign:
- Feign是Spring Cloud组件中的一个轻量级RESTful的HTTP服务客户端,Feign内置了Ribbon,用来做客户端负载均衡,去调用服务注册中心的服务。Feign的使用方式是:使用Feign的注解定义接口,调用这个接口,就可以调用服务注册中心的服务。
openfeign:
- OpenFeign是Spring Cloud 在Feign的基础上支持了SpringMVC的注解,如@RequesMapping等等。OpenFeign的@FeignClient可以解析SpringMVC的@RequestMapping注解下的接口,并通过动态代理的方式产生实现类,实现类中做负载均衡并调用其他服务
基本使用
1、导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-openfeign</artifactId>
<version>2.2.9.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>2、创建接口,并添加 @FeignClient 注解
@FeignClient(name = "cmp-workorder")
public interface WorkOrderFeign {
@GetMapping("/workorder/pendingWorkorderList")
DataPage<WorkorderVo> pendingWorkorderList();
} 3、启动类中添加 @EnableFeignClients 注解,并确保能够扫描到对应的 feign,并为其代理注册为 bean
4、后续在其他地方直接依赖注入 WorkOrderFeign 这个 bean 之后就可以直接使用方法
5、当调用 pendingWorkorderList() 方法时,会往 @FeignClient 注解指定的服务发送请求,路径为 @GetMapping 注解中的路径
@Autowired
private WorkOrderFeign workOrderFeign;
public void test() {
workOrderFeign.pendingWorkorderList();
} Feign.Builder
介绍
Feign.Builder是Feign的构建器,用于构建Feign客户端实例。
用法
1、创建接口
import feign.RequestLine;
public interface UserFeign {
@RequestLine("POST /hello")
String hello();
} 2、动态创建 feign
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test() {
UserFeign userFeign = Feign.builder()
.target(new Target.HardCodedTarget<>(UserFeign.class, "http://localhost:8080"));
String res = userFeign.hello();
return res;
} 这样就可以动态创建 feign 并指定服务为 http://localhost:8080
除此之外还可以动态指定 feign 的其他配置
FeignClient 注解
常用属性如下:
name、value:用于指定调用的服务名,可以是 nacos 中的服务名,会使用 ribbon 进行服务的负载均衡
url:直接指定对应的请求地址,优先级会比 name、value 高,一般用于本地调试
contextId:指定这个 bean 的名称
fallbackFactory:用于指定调用失败时的处理类
configuration:用于指定配置类
@Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) @Documented @Inherited public @interface FeignClient { /** * @return the name of the service with optional protocol prefix */ @AliasFor("name") String value() default ""; /** * @return the service id with optional protocol prefix */ @Deprecated String serviceId() default ""; /** * @return bean name instead of name if present */ String contextId() default ""; /** * @return The service id with optional protocol prefix. Synonym for { @link #value() * value} . */ @AliasFor("value") String name() default ""; /** * @return the <code>@Qualifier</code> value for the feign client. */ @Deprecated String qualifier() default ""; /** * @return the <code>@Qualifiers</code> value for the feign client. */ String[] qualifiers() default { } ; /** * @return an absolute URL or resolvable hostname (the protocol is optional). */ String url() default ""; /** * @return whether 404s should be decoded instead of throwing FeignExceptions */ boolean decode404() default false; /** * @return list of configurations for feign client */ Class<?>[] configuration() default { } ; /** * @return fallback class for the specified Feign client interface */ Class<?> fallback() default void.class; /** * @return fallback factory for the specified Feign client interface */ Class<?> fallbackFactory() default void.class; /** * @return path prefix to be used by all method-level mappings. Can be used with or * without <code>@RibbonClient</code>. */ String path() default ""; /** * @return whether to mark the feign proxy as a primary bean. Defaults to true. */ boolean primary() default true;
}
## 配置请求头(header)
1、在 @FeignClient 注解中指定配置类
```java
@FeignClient(name = "cmp-workorder", configuration = FeignConfig.class)
public interface WorkOrderFeign {
} 2、编写配置类代码,实现 RequestInterceptor 接口,获取当前请求的请求头信息,设置给 feign 代理对象中的 request
public class FeignConfig implements RequestInterceptor {
@Override
public void apply(RequestTemplate template) {
RequestAttributes requestAttributes = RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
if (requestAttributes == null) {
log.info("====FeignConfig requestAttributes is null.");
return;
}
HttpServletRequest request = ((ServletRequestAttributes) requestAttributes).getRequest();
Enumeration<String> headerNames = request.getHeaderNames();
if (headerNames != null) {
while (headerNames.hasMoreElements()) {
String name = headerNames.nextElement();
Enumeration<String> values = request.getHeaders(name);
while (values.hasMoreElements()) {
String value = values.nextElement();
template.header(name, value);
}
}
}
}
} 设置消息转换器
直接创建对应的 bean 即可,替换掉 feign 中默认的消息转换器
@Bean
public Encoder feignEncoder() {
return new SpringEncoder(feignHttpMessageConverter());
}
/**
* 设置为fastjson
*
* @return
*/
private ObjectFactory<HttpMessageConverters> feignHttpMessageConverter() {
final HttpMessageConverters httpMessageConverters = new HttpMessageConverters(this.getFastJsonConverter());
return () -> httpMessageConverters;
}
private FastJsonHttpMessageConverter getFastJsonConverter() {
FastJsonHttpMessageConverter converter = new FastJsonHttpMessageConverter();
List<MediaType> supportedMediaTypes = new ArrayList<>();
MediaType mediaTypeJson = MediaType.valueOf(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_VALUE);
supportedMediaTypes.add(mediaTypeJson);
converter.setSupportedMediaTypes(supportedMediaTypes);
FastJsonConfig config = new FastJsonConfig();
config.getSerializeConfig().put(JSON.class, new SwaggerJsonSerializer());
config.setSerializerFeatures(SerializerFeature.DisableCircularReferenceDetect);
converter.setFastJsonConfig(config);
return converter;
} feign 的创建过程
1、从 @EnableFeignClients 注解开始,进入后会看到导入了 FeignClientsRegistrar 类用于注册 feign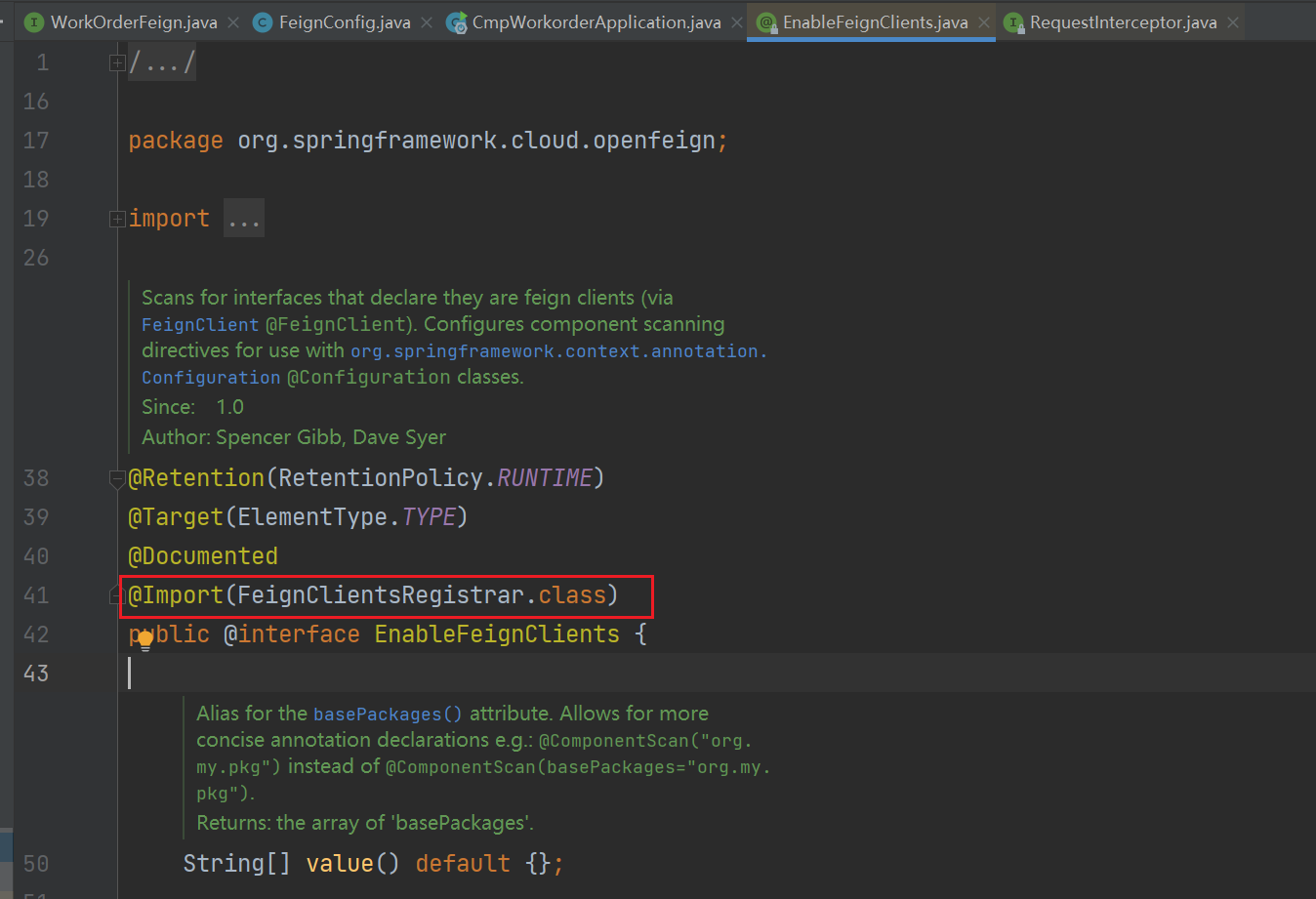
2、而 FeignClientsRegistrar 又实现了 ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar 接口,用于创建 beanDefinition。而ResourceLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware 分别用于注入 ResourceLoader 加载器和 Environment 环境信息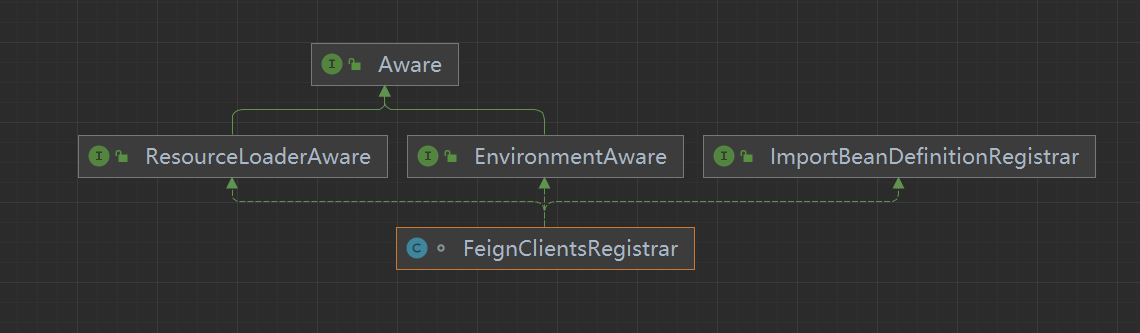
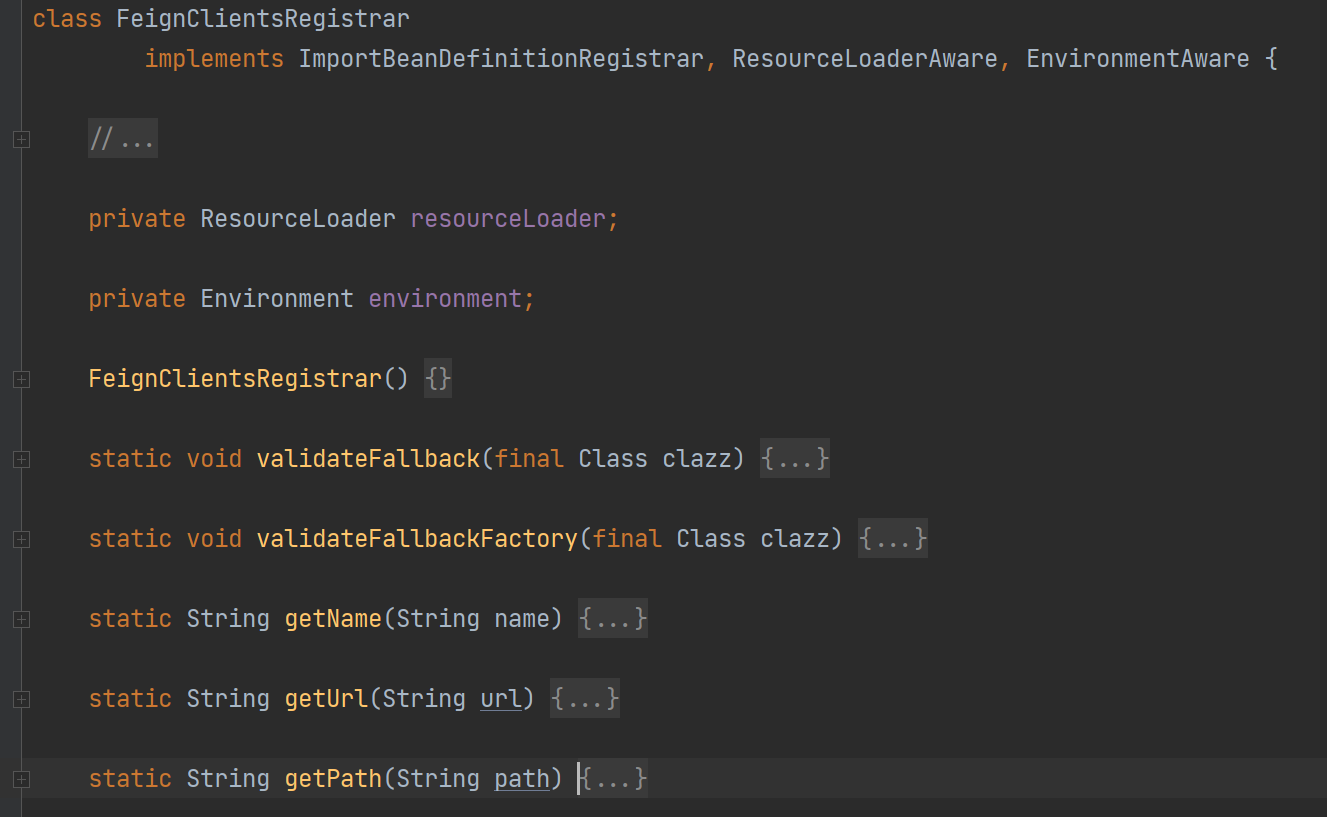
3、直接查看 registerBeanDefinitions 注册 bean 的方法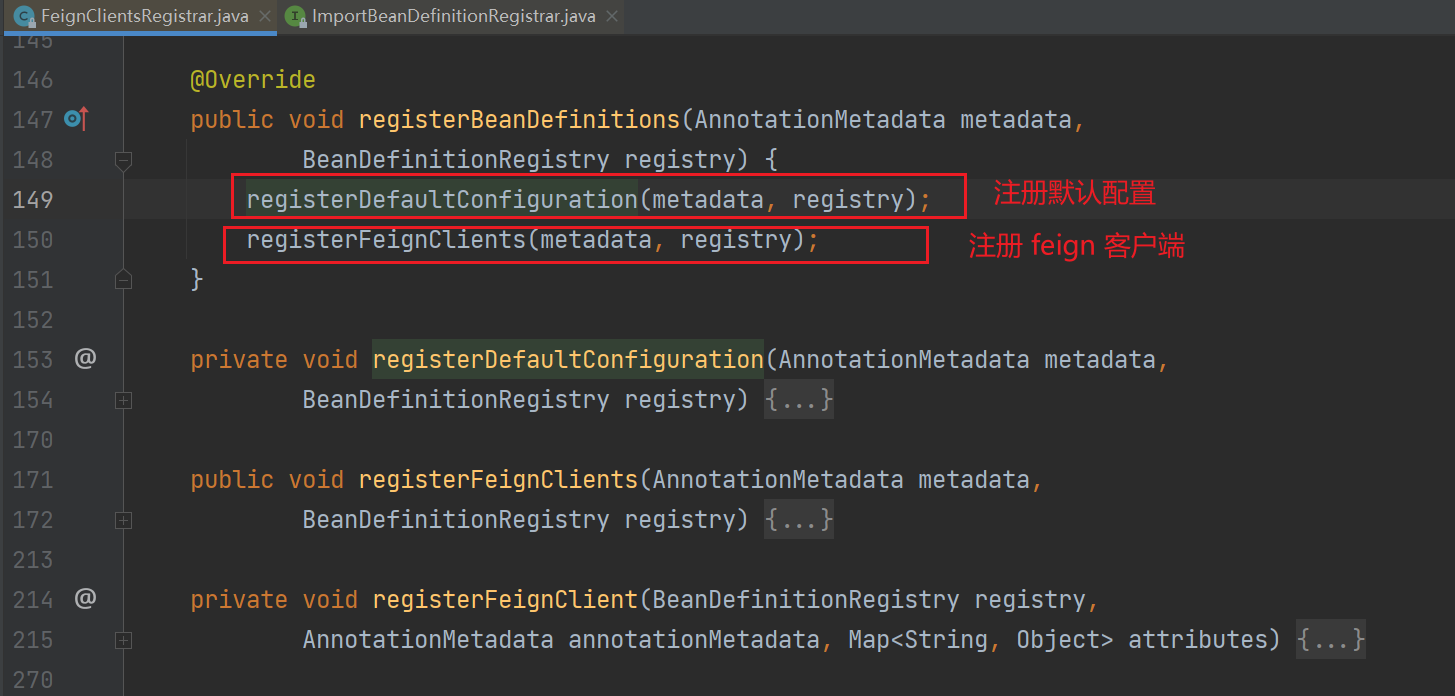
registerDefaultConfiguration() 方法用于加载注解中配置的 defaultConfiguration 默认配置类(暂时不看)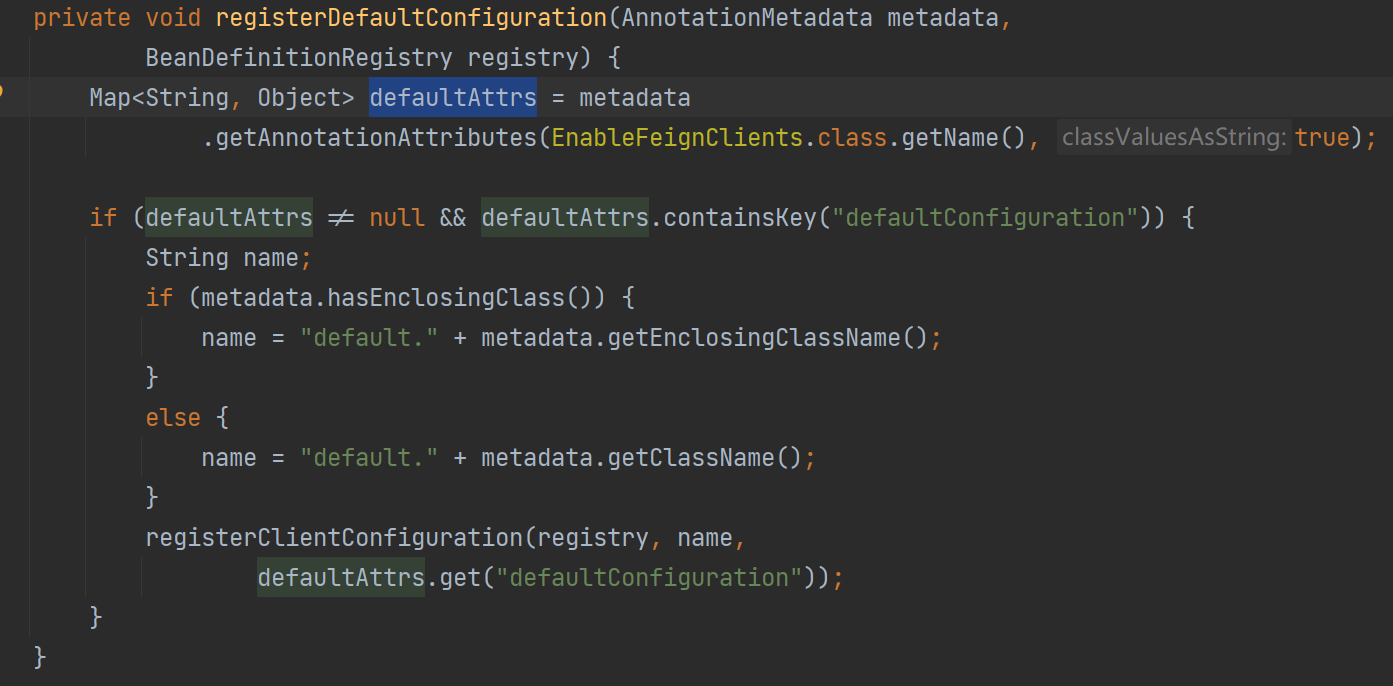
registerFeignClients() 方法,会先解析注解中的值 clients,如果指定,则直接注册这部分 feign;否则会获取扫描路径并扫描具有 @FeignClient 注解的类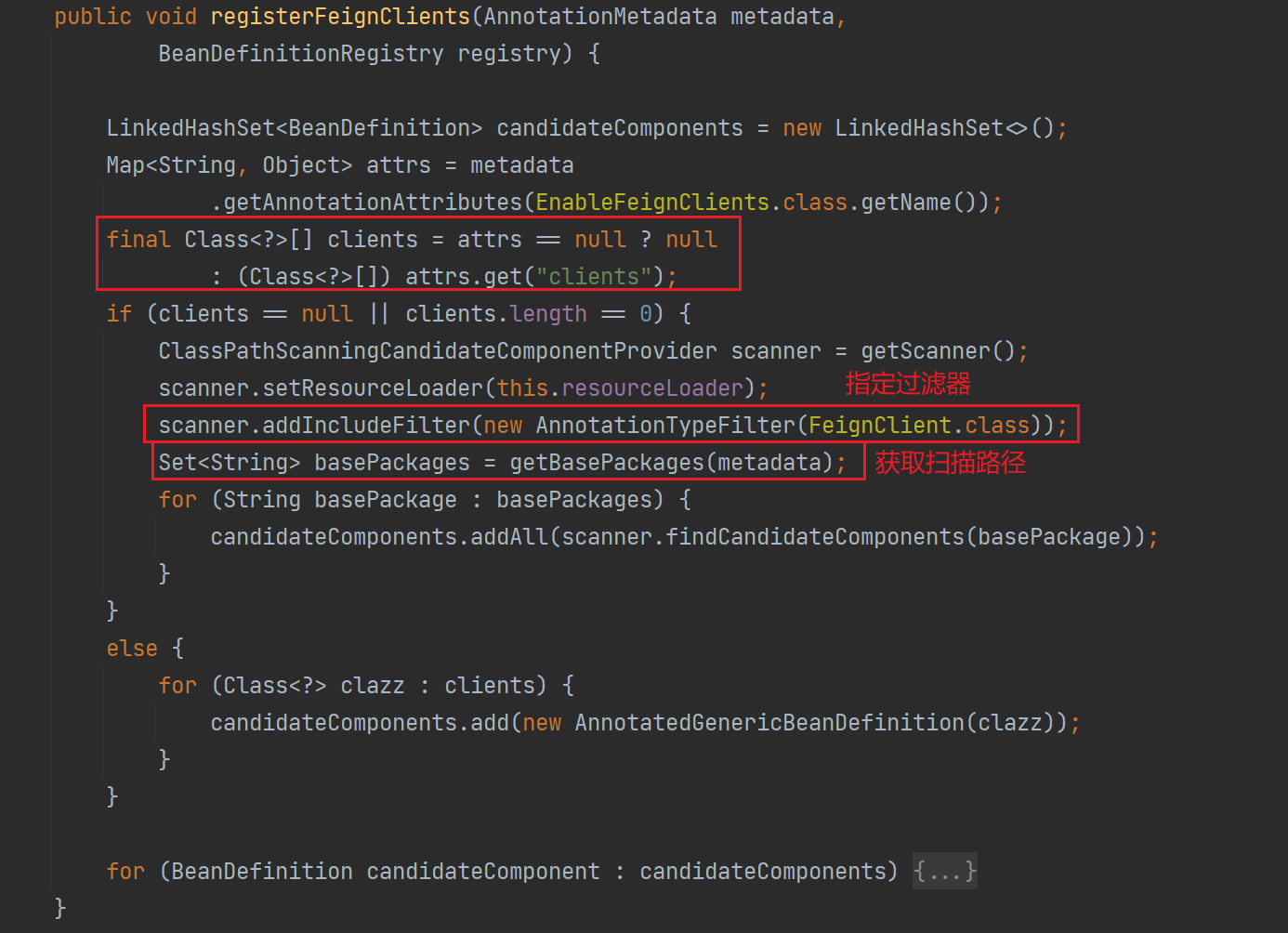
而在获取扫描路径的方法 getBasePackages() 中,则会根据如下规则进行获取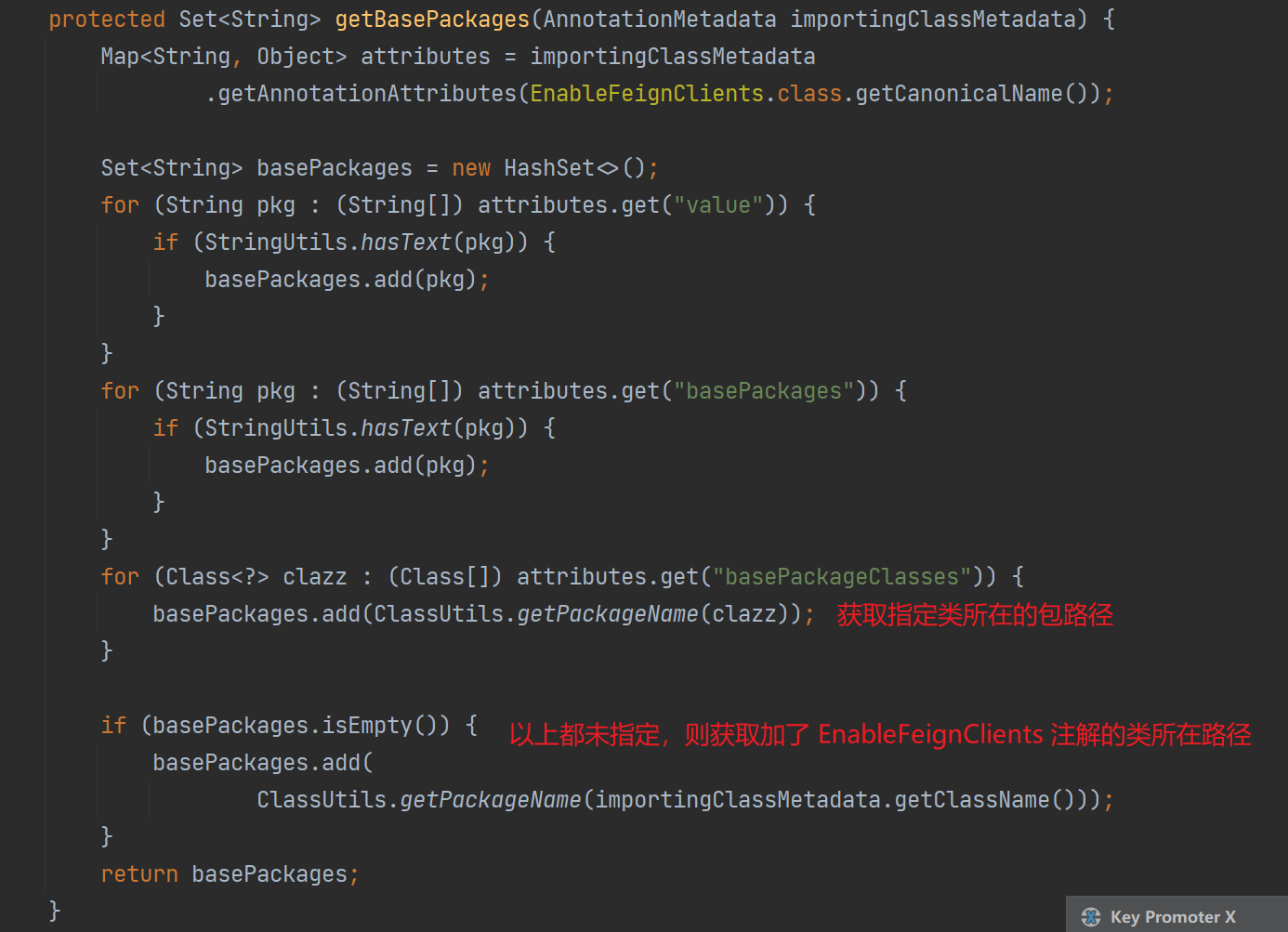
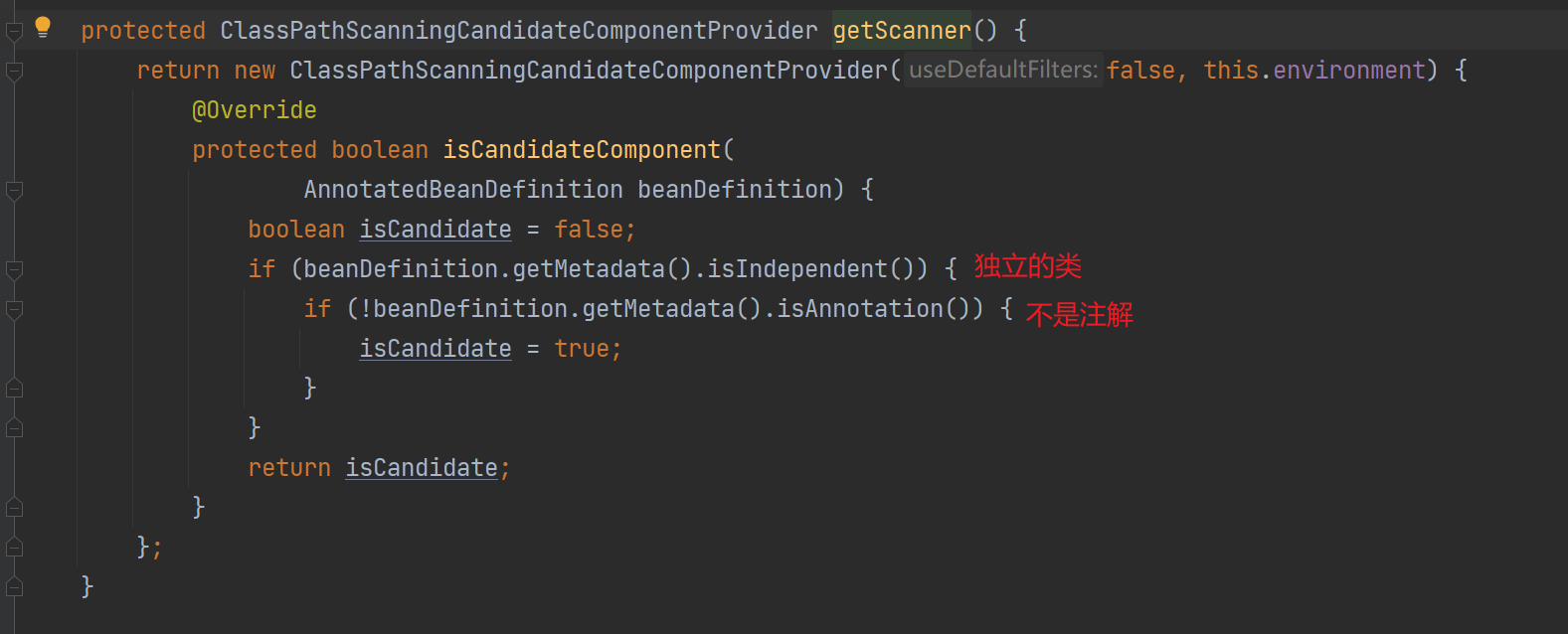
4、扫描路径,并获取候选 bean,详细的就不看了,这部分就是直接扫描对应路径下的,独立的且非注解,并具有 @FeignClient 注解的类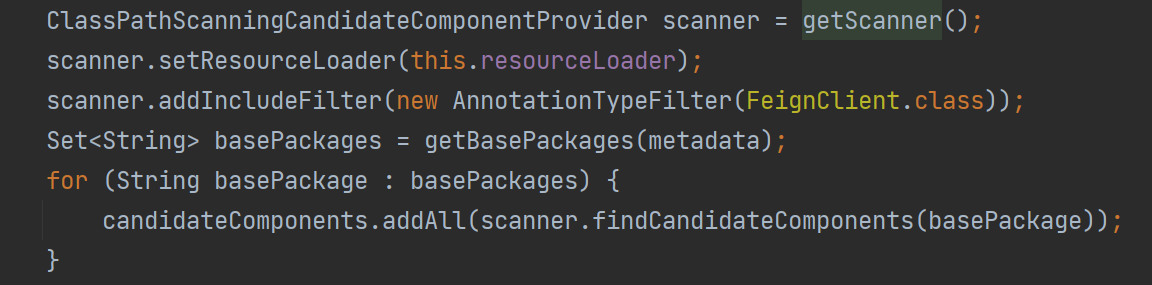
5、开始处理候选 bean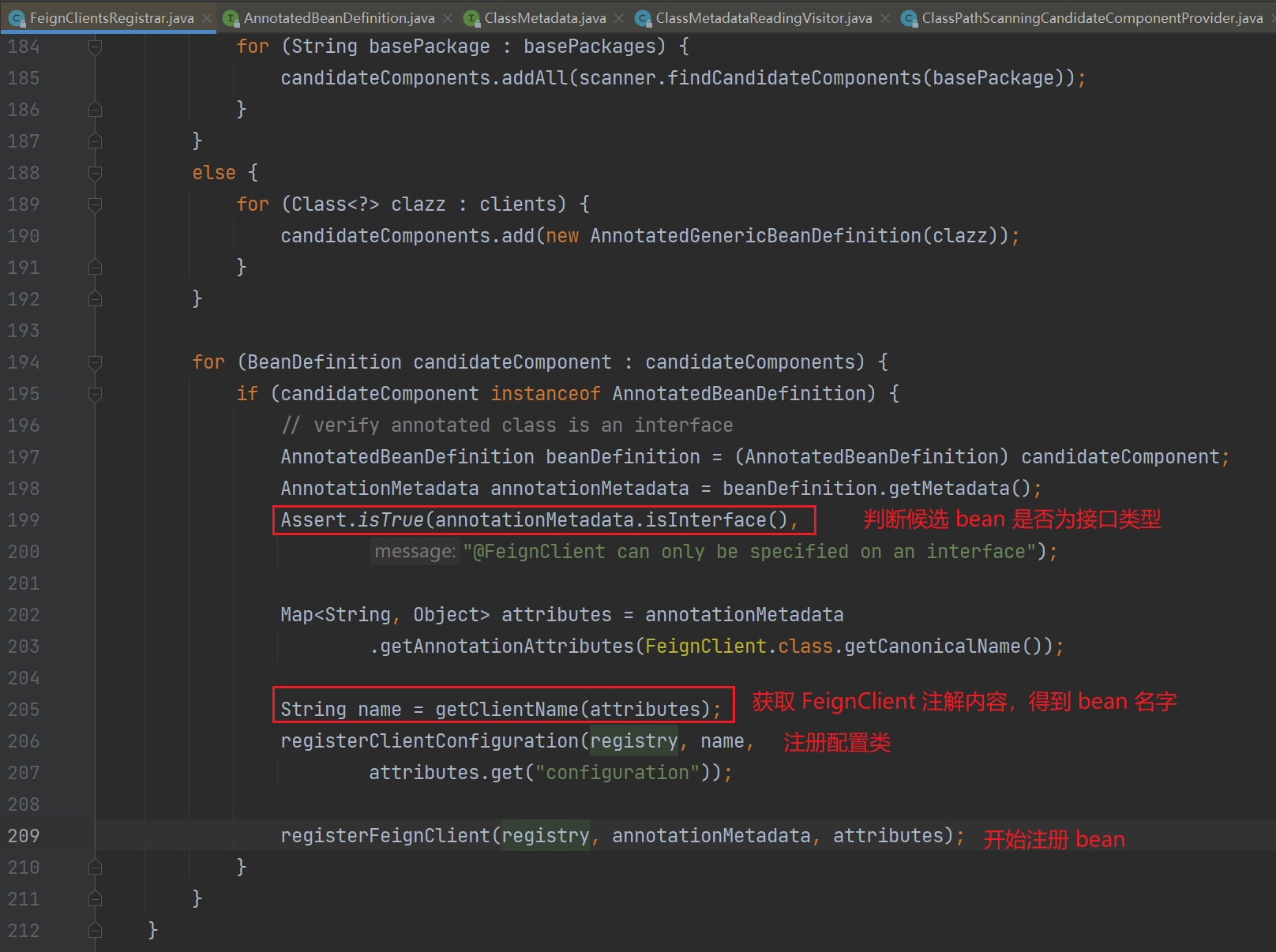
获取 bean 名字,字段的优先级如下,contextId 优先级最高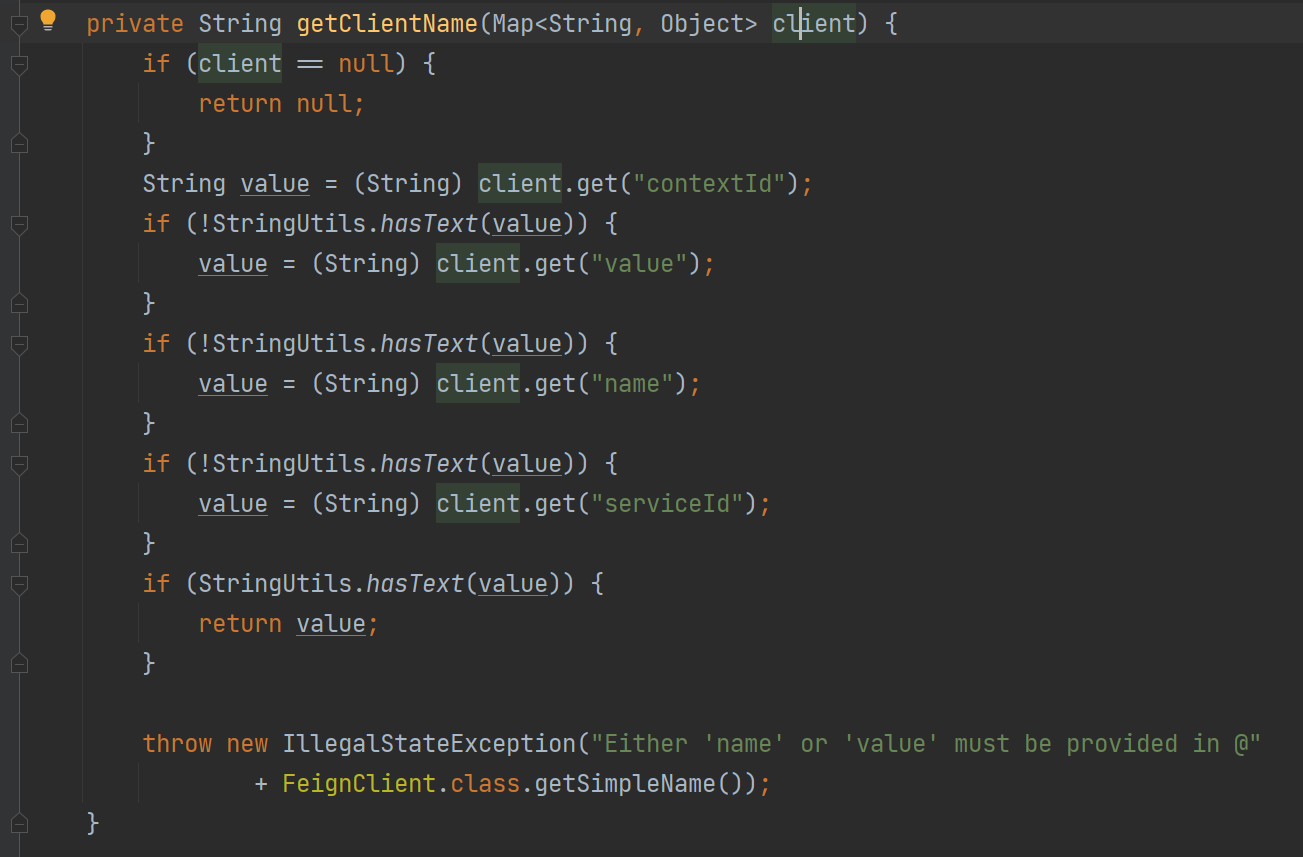
注册配置类,分别为每个 feign 注册一个配置类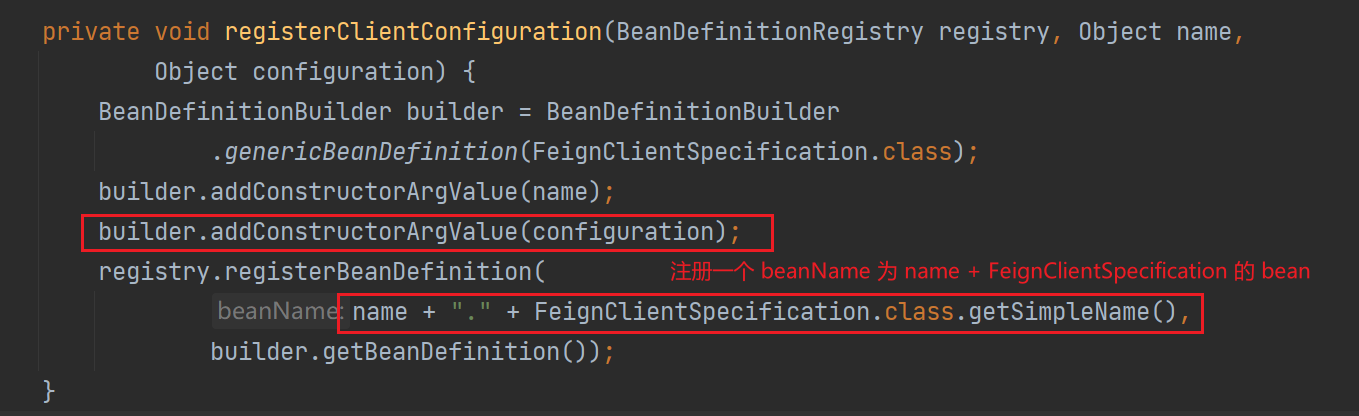
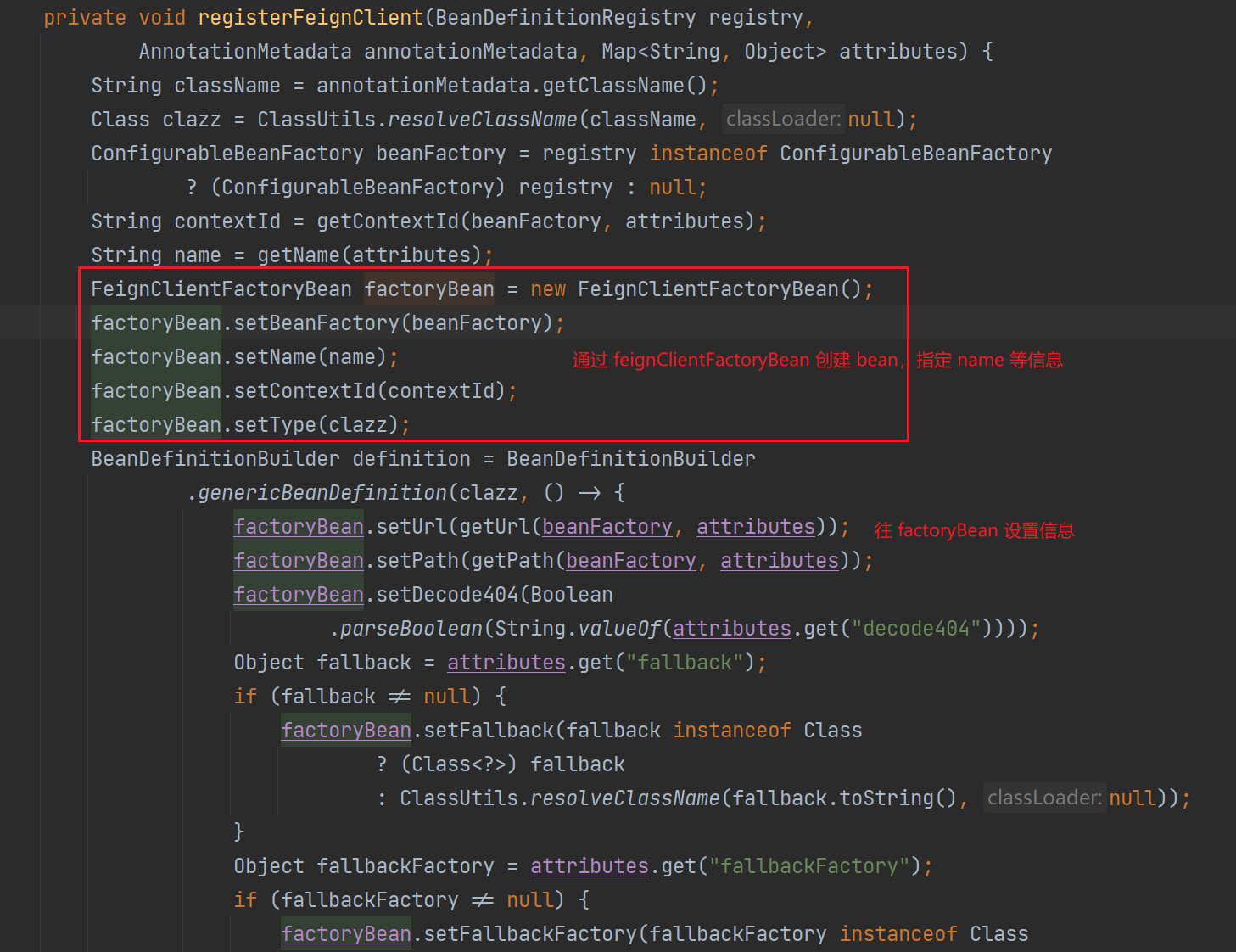
注册 bean,通过 FeignClientFactoryBean 创建对应的代理类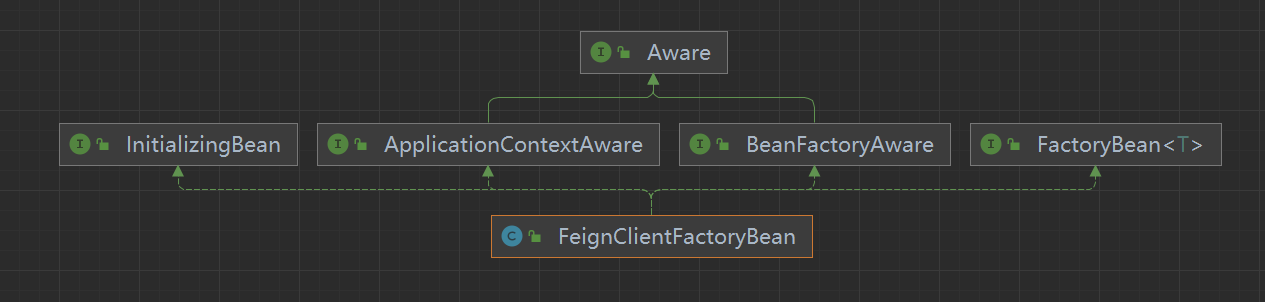
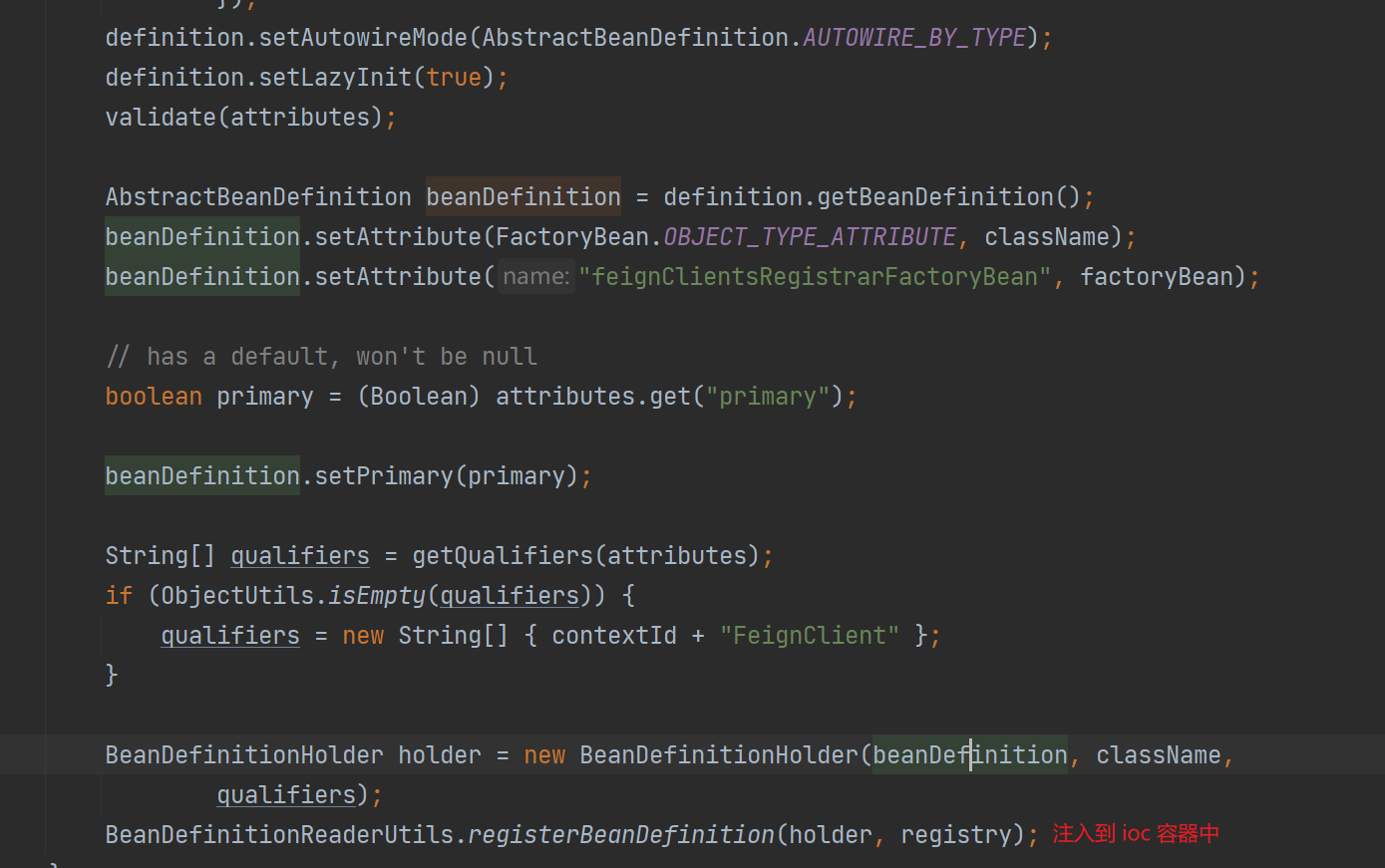
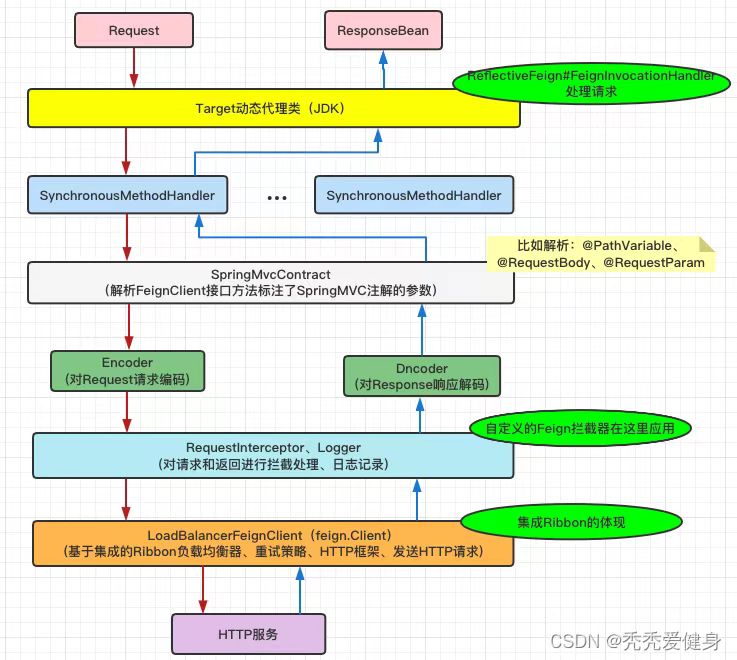
feign 的请求流程
面试题
- 本文链接:https://lxjblog.gitee.io/2024/07/26/OpenFeign/
- 版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均默认采用 许可协议。